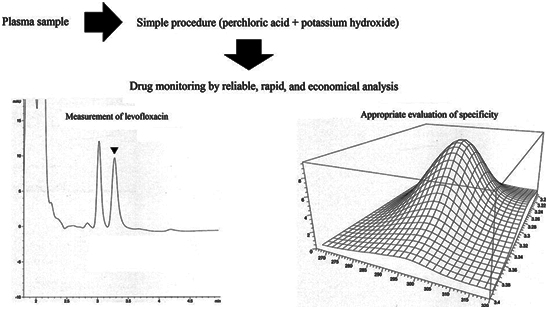
Levofloxacin monitoring is recommended to obtain clinical cure and low incidence of antimicrobial resistance. During the monitoring procedure, levofloxacin should be measured in plasma samples and several assays are reported for this purpose. However, those methods do not have all of the characteristics for an accessible and reliable drug monitoring. For this reason, we develop a method that has all of the essential characteristics for levofloxacin monitoring. The procedure of validation was done in terms of Food and Drug Administration guidelines. Subsequently, assay was applied in plasma samples obtained from healthy volunteers with a single oral administration of levofloxacin as well as patients with respiratory diseases under levofloxacin therapy. Levofloxacin was extracted from samples using only two precipitation steps. The assay had a rapid run time (5 min), adequate sensitivity (0.05 μg/ml of lower limit of quantification), and acceptable parameters of validation. Moreover, compound identities were supported using three dimensional spectra and purities were confirmed employing similarity factors (values > 900). Variable concentrations of levofloxacin in samples were observed during the application. Levofloxacin is successfully quantified using our method that shows reliable results, appropriate range, rapid analyses, and cost-effective measurements under a simple and easy technique while all prior methods did not have it all together. Consequently, the asssay is a valuable tool for routine drug monitoring.
Aragon-Martinez O H, Isiordia-Espinoza M A, Galicia O, et al.Clinical Biochemistry, 2016, 465:1-4.













